
What are anxiety disorders?
They’re a mental health issue driven by feelings of worry, anxiety, or fear. These feelings are so persistent or strong that they interfere with a person’s daily activities, according to the Cleveland Clinic. The disorders impact about 40 million adult Americans; anxiety-related issues are the most prevalent mental illness in the United States. The disorders tend to start in childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood, and they’re more common in women than in men.

Thyroid issues
Hyperthyroidism — overactive thyroid — raises your metabolic rate, which can lead to symptoms like a rapid heart rate and weight loss, reports the Mayo Clinic. Your doctor can diagnose the condition with a blood test, and then advise you on the best course of treatment.

Heart disease
Cardiac symptoms like angina — heart pain — and arrhythmias — uneven heart rate — can trigger anxiety symptoms, says Randi E. McCabe, PhD, a clinical psychologist at St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton in Canada and a professor in the Department of Psychiatry of Behavioural Neurosciences at McMaster University in Canada. Be sure to see a doctor right away if you shortness of breath or excessive fatigue along with heart pain, Dr. McCabe warns, though don’t assume the worst: Doctors at the Montreal Heart Institute reported in the American Journal of Medicine that about a quarter of 441 patients who came to the ER because of chest pain were suffering from panic disorder, not a heart ailment.

Lack of sleep
While insomnia itself can be stressful, poor sleep can increase your risk of anxiety: A study in the Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychology found that sleep deprivation increases depression and general distress. In fact, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA), sleep deprivation and chronic insomnia can cause an anxiety-related disorder.
Social media may also be ruining your sleep. Find out how.
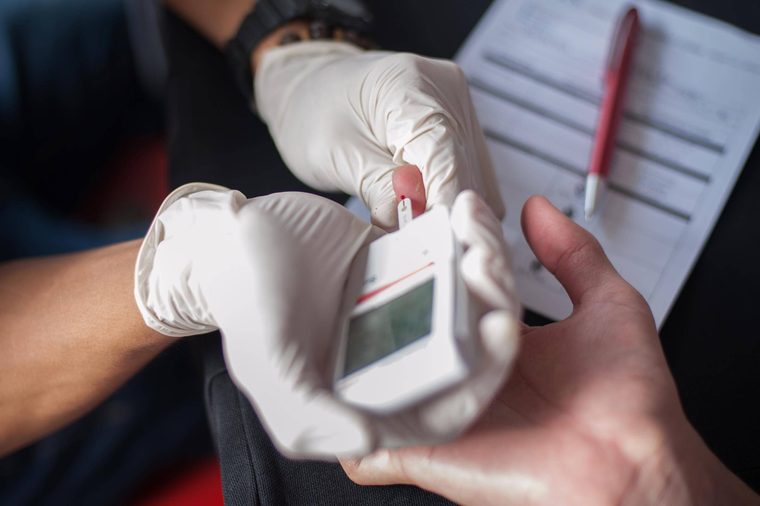
Diabetes
High or low blood sugar can set you up for anxiety, says Dr. McCabe. Research published in Medical Science Monitor suggests that 32 percent of people with type 2 diabetes will be diagnosed with an anxiety-related disorder.
Simple Mini-Steps to Improve Your Diet When You Have Diabetes

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Approximately one in five adults in the United States has IBS, according to the ADAA, and they point out that the colon is, in part, controlled by the nervous system — which of course is uniquely sensitive to stress. Anxiety may also creep in when people fear their condition and how it limits their life—not feeling safe in public, for example, because they may not be able to make it to a restroom on time, says Dr. McCabe. Here’s what everyone should know about coping with anxiety.

Asthma
The shortness of breath and wheezing people get during an asthma attack can drive up the risk of anxiety, reports the American Psychological Association. “Your existing anxiety may be triggered by the internal sensations that come along with an anxiety attack,” says Robert Duff, Ph.D., a licensed psychologist and author of the Hardcore Self Help book series.
You Might Not Actually Have Asthma After All, New Study Finds
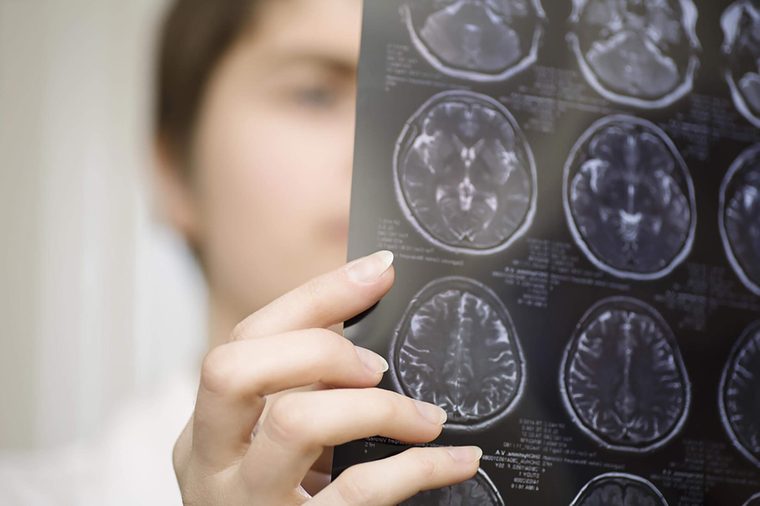
A neurological disorder
Well in advance of other symptoms, anxiousness can signal conditions such as brain tumors and temporal lobe epilepsy, according to a report in the journal Psychotherapy and Psychodynamics. Researchers from Italy and Buffalo found that patients can develop anxiety disorders years before doctors diagnose a neurological issue.
Anemia
Your red blood cells deliver oxygen to muscles, and when you run low — or the cells aren’t working properly — you can end up feeling fatigued. Your pulse may increase to help make up the oxygen loss, and that can create a sense of anxiousness.
Nutritional deficiencies
Zinc helps maintain the immune system, heal wounds, and support normal growth — and if you’re low, numerous studies suggest the deficiency could make you feel anxious. The mineral helps support calming substances in the brain. A vitamin B12 deficiency may also increase anxiety since the nutrient helps support a healthy nervous system, according to Psychology Today.
Learn about these trusted home remedies for anxiety relief.
Pancreatic cancer
The connection is as strange as it is upsetting: A study has found that as many as half of people diagnosed with pancreatic cancer had symptoms and signs of anxiety and depression beforehand, though it’s unclear why. This type of cancer is thankfully rare: The American Cancer Society says that the average lifetime risk of pancreatic cancer for men is about 1 in 65.
Tinnitus
This condition creates a chronic ringing due to faulty nerve signals from the ear, and it leaves sufferers vulnerable to anxiety. “Tinnitus increases agitation, making it harder to relax,” says Paul Coleman, PsyD, a psychologist and author of Finding Peace When Your Heart Is in Pieces. “There is no such thing as pure quiet when you have tinnitus.” The condition can prevent sound sleep since it’s often most notable in the quiet of the night, notes Dr. Coleman. Often a white-noise machine can help drown out the ringing.

Substance-induced anxiety disorder
People with this disorder may experience anxiety as a result of taking medications, being exposed to a toxic substance, drug abuse, or withdrawing from drugs. They can feel tense or jittery, says Dr. McCabe. The ADAA says that about 20 percent of people with an alcohol or substance abuse issue also have a mood disorder.

How are these disorders treated?
The treatment you’ll get depends on the type of disorder you’re struggling with. A mental health practitioner might recommend one or a combination of therapies, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Your doctor might prescribe an anti-anxiety drug, psychotherapy (where you discuss potential sources of your anxiety and how to deal with them), or cognitive behavior therapy, in which you learn to recognize and change the thoughts and actions that lead to your feelings.
Here’s why you might want to consider getting more frequent massages!
