How to Do a Self Breast Exam
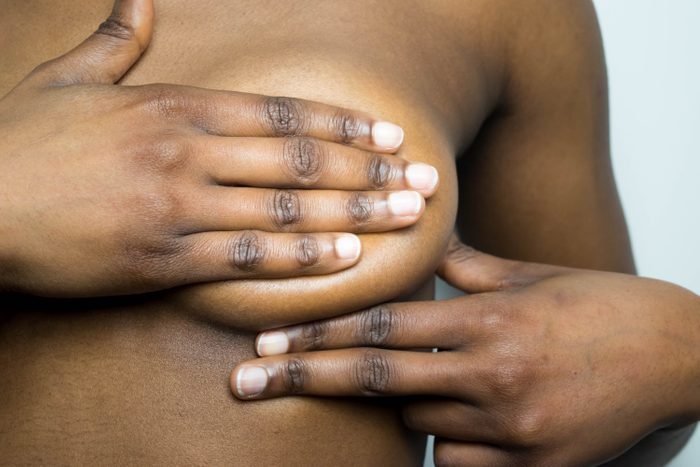
Along with routine screenings, frequent at-home examinations are the key to knowing your norm and catching any concerning changes.
In Canada, breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second-most common cause of death from cancer among women. On average, 75 Canadian women are diagnosed with breast cancer every day.
Despite how common breast cancer is, the early signs and symptoms can be hard to spot. While every province has a breast cancer screening program, they don’t always catch breast cancer early. (This is especially true if your province only mandates screenings every two years—a lot can change in that time.) And we know that the earlier breast cancer is detected, the higher the likelihood of survival and recovery.
Regular screenings and attending all your physical check-ups are the most important tools for detecting breast cancer, but at-home breast exams are also a useful way to catch any abnormalities. Here is why regularly examining your breasts is important, as well as how to do a breast self-exam.
(Related: How to Embrace Your Sexuality After a Diagnosis)
Why are at-home breast self-exams so important?
Gaining awareness of what’s normal for your body and noticing (either on sight or by feel) when there’s been a change means you can promptly report it to your healthcare provider. “You can’t know there’s been a change unless you know what your normal breast tissue feels like — and you’d only know if you’re doing breast self-exams often,” says Dr. Paula Gordon, a clinical professor at the University of British Columbia.
That said, Gordon also emphasizes that there are many cancers that aren’t detectable by a self-exam and that at-home breast examinations should augment regular mammograms and other tests. “Understanding your entire body and anything that changes is important, but first and foremost, discuss any changes with your doctor who is familiar with your risk factors,” adds Cathy Ammendolea, the Chair of the Board of the Canadian Breast Cancer Network.
How do I examine my breasts at home?
Before jumping into the how, it’s good to set up the when: your breasts’ size, texture and lumpiness fluctuates depending on where you’re at in your menstrual cycle, making it tricky to know what your norm is. If you’re still menstruating, Gordon recommends doing your breast self-exam a few days after your period. Before your period, it’s normal for your breast tissue to feel lumpier and sore. “This ensures you’re comparing apples to apples each time,” says Gordon. If you’ve gone through menopause, give yourself an exam periodically.
To perform a self-exam, start with the visual check. Stand in front of your mirror, topless, and turn side to side, checking for lumps and changes in your nipples. Then, lift your hands above your head. After that, place your hands on your hips and flex your chest muscles. Both moves can help you see lumps that you wouldn’t otherwise see.
(Related: Sofia Vergara’s Thyroid Cancer Experience Is an Important Reminder for All)
Next is the feel test. Unless you have really small breasts, you should be doing your self-exam like a breast surgeon does it: lying back at about a 30-degree angle (for example, lying down in bed with your head propped up on a few pillows). Keep your fingers flat and bent slightly at the knuckles, use the undersurface of your fingers to squish your breast tissue against your ribcage. Then, feel for lumps and any changes by going around the circumference of your breast to the nipple and then feeling the nipple as well. Finally, check your armpits, where there may be enlarged lymph nodes. Reach your hand over to hold onto the opposite shoulder and then, using your other hand, squish the tissue and fat of your armpit against your rib cage and feel for any lumps.
Gordon suggests checking out this video by breast surgeon Dr. Liz O’Riordan as a guide:
What sorts of breast changes should I be looking out for?
Generally, when doing a visual examination (ie., looking at yourself topless in a mirror) you should check for any lumps, redness, dimpling, skin sores, growing veins, thick skin and pores that look more prominent—“we call it ‘skin of an orange,’ because your skin looks like an orange peel,” says Gordon. Notice if your nipple is sunken or if there’s a crust on the nipple. Also, look out for any discharge that comes out on its own. Clear or bloody discharge that spontaneously seeps without your intervention should be checked out by your doctor, says Gordon. If you have discharge, but you really need to force it in order for it to come out, that usually isn’t a cause for concern.
Then, when you’re touching your breast, feel for any abnormal textures, lumps or areas of unusual firmness. “Everyone has texture or lumpiness in their breast, but it’s unique to us,” says Gordon. “People who do periodic breast self-exams are experts in what’s normal for them. We intuitively remember what the normal texture feels like and if we notice a slight change, that’s when the alarm bells go off.”
(Related: What Doctors Want You to Know About Breast Cancer)
What should I do if I do discover a concerning change in my breast?
If you notice something different in your breast tissue, contact your healthcare provider and ask for a mammogram or another form of testing. If you have dense breast tissue (which you can find out when you get a mammogram), it’ll make it harder to detect some forms of breast cancer. So, make sure you ask your doctor for an alternate form of breast cancer screening (like an ultrasound) in addition to a mammogram, depending on your age. Ultrasound would be a reasonable first test for women younger than 30-35.
Next: The Canadian Provinces with the Highest Rates of Cancer